How to install MongoDB 5 on Ubuntu 20.04
MongoDB is one of the popular open source and document oriented database systems. It belongs to a family of databases called NoSQL, which is different from the traditional table based SQL databases. It makes use of collections, each having multiple documents, and allows the user to store data in a non relational format. Data is stored in flexible, JSON-like documents where fields can vary from document to document.
MongoDB is highly scalable and flexible. It is used for building modern applications that require powerful, mission critical and high availability databases.
Installing MongoDB
MongoDB is available and can be installed using the apt packaging system. First you need to update your system repository in order to install MongoDB.
sudo apt-get update
Now, install the MongoDB with the following apt command:
sudo apt install -y mongodb
Apt manager will install the package and all the dependencies.
To check the service status use the command:
sudo systemctl status mongodb
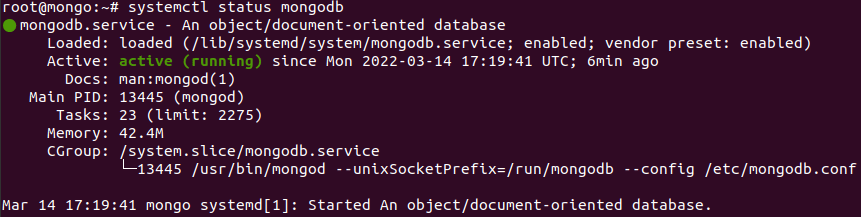
Additionally you can check if the installation process is done correctly and everything is working fine:
mongo --eval 'db.runCommand({ connectionStatus: 1 })'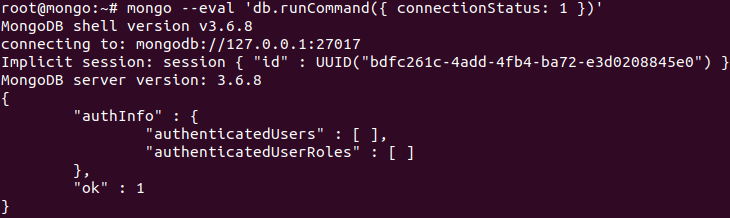
The value "ok" : 1 indicates that the server is working properly with no errors.
Managing the MongoDB Process
Once your database server is up and running you can use the following commands to manage the mongodb process:
sudo systemctl [stop|start|restart|disable|enable] mongodb
Configuring MongoDB
MongoDB default configuration file is located at /etc/mongodb.conf. By default, each user will have access to all databases and perform any action. For production environments, it is recommended to enable the MongoDB authentication.
Authentication
To enable the authentication uncomment the auth directive in the config file:
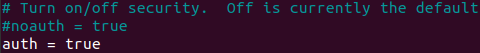
After that restart mongodb service
sudo systemctl restart mongodb
Creating administrative MongoDB user
If you enabled the MongoDB authentication, you’ll need to create an administrative user that can access and manage the MongoDB instance.
Access the mongo shell:
mongo
From inside the MongoDB shell connect to the admin database:
use admin
Now, create a user for your MongoDB installation setting desired username and password:
db.createUser({ user:"hibit", pwd:"hibit_password", roles:[{ role:"userAdmin", db:"admin" }] })We've used userAdmin built-in role but you can find more, with detailed descriptions, on the official MongoDB documentation: built-in roles.
Exit from the MongoDB console:
quit()
Checking MongoDB connection
Try to connect to MongoDB instance using the user which you have created earlier:
mongo -u hibit -p --authenticationDatabase admin
You will be asked to provide the password as shown below:
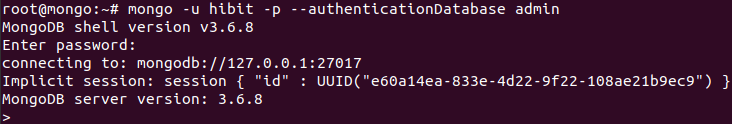
Remote access
By default, MongoDB can only be accessed locally. To be able to access the database remotely we will make a small change on the configuration file to include MongoDB server IP address (or hostname) as shown below:
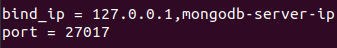
After that restart mongodb service
sudo systemctl restart mongodb
The remote access to the server IP/hostname via port 27017 is now open.
You can perform a quick test of the response pointing to the MongoDB IP/hostname (including the port) in your browser address bar:
It looks like you are trying to access MongoDB over HTTP on the native driver port.
Remote access firewall
Having MongoDB exposed without any additional security is risky. We recommend you to allow only the trusted remote IP addresses on the firewall.
sudo ufw allow from trusted-ip to any port 27017
This will block remote incoming connections from non trusted IP addresses.
Conclusion
In the above guide, we've learned how to install and configure MongoDB server on Ubuntu 20.04. For more information, you can visit the MongoDB documentation and find all available options for the tuning.



0 Comments