Install and configure Nginx on Ubuntu
Nginx is open source software for web serving, reverse proxying, caching, load balancing, media streaming, and more. It started out as a web server designed for maximum performance and stability. In addition to its HTTP server capabilities, Nginx can also function as a proxy server for email (IMAP, POP3, and SMTP) and a reverse proxy and load balancer for HTTP, TCP, and UDP servers.
Installing Nginx
Nginx is available and can be installed using the apt packaging system:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install nginx
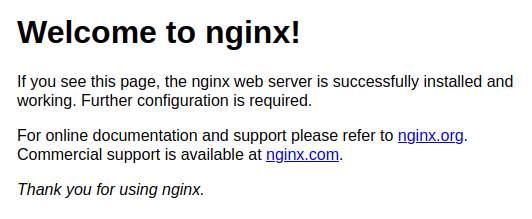
Package manager will install the server and all the dependencies. You can point your browser to your server IP address (or localhost). You should see this page:
Configure the Firewall
For additional security some settings must be applied to the firewall software to allow access to the service. Nginx is automatically registered as a service with ufw upon installation making it easy to allow Nginx access.
You can list available configurations with the following command:
sudo ufw app list
You should get a listing of the application profiles:
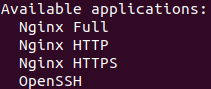
There are three profiles available for Nginx:
Nginx Full: this profile opens both port 80 (normal, unencrypted web traffic) and port 443 (TLS/SSL encrypted traffic)
Nginx HTTP: this profile opens only port 80 (normal, unencrypted web traffic)
Nginx HTTPS: this profile opens only port 443 (TLS/SSL encrypted traffic)
In our case we select the FULL profile and allow traffic on ports 80 and 443:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'

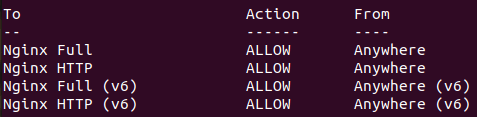
Enable ufw and verify the change by typing:
sudo ufw enable && ufw status
Managing the Nginx Process
Now that you have your web server up and running you can use the following commands to manage the nginx process:
sudo systemctl [stop|start|restart|reload|disable|enable] nginx
Files and directories
We already have the web server but... where do we upload the files? The structure of the files is clear:
Content
/var/www/html: The actual web content, which by default only consists of the default Nginx page.
Configuration
/etc/nginx: The Nginx configuration directory. All of the Nginx configuration files are here.
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf: The main Nginx configuration file. This can be modified to make changes to the Nginx global configuration.
/etc/nginx/sites-available/: directory where separated site settings can be saved.
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/: directory where we link one of the previous configurations and also mark them as active.
Logs
/var/log/nginx/access.log: every request to the web server is recorded in this log file.
/var/log/nginx/error.log: all Nginx errors will be recorded in this log.



0 Comments